JNCC:- (Joint Nature Conservation Committee)"The Joint Nature Conservation Committee (JNCC) is the statutory adviser to Government on UK and international nature conservation. Its work contributes to maintaining and enriching biological diversity, conserving geological features and sustaining natural systems."
SSSI:- (Site of Special Scientific Interest)SSSIs are the basic building block of site-based nature conservation and legislation. Most other legal natural/geological conservation designations in Great Britain are based upon them. they are given their designation by the
Wildlife and Countryside Act 1981.
SAC:- (Special Area of Conservation) These are strictly protected sites designated under the EC Habitats Directive. Article 3 of the
Habitats Directive requires the establishment of a European network of important high-quality conservation sites that will make a significant contribution to conserving the 189 habitat types and 788 species identified in Annexes I and II of the Directive (as amended). The listed habitat types and species are those considered to be most in need of conservation at a European level (excluding birds). Of the Annex I habitat types, 78 are believed to occur in the UK. Of the Annex II species, 43 are native to, and normally resident in, the UK.
SPA:- (Special Protection Areas)Special Protection Areas (SPAs) are strictly protected sites classified in accordance with Article 4 of the
EC Directive on the conservation of wild birds (79/409/EEC), also known as the
Birds Directive, which came into force in April 1979. They are classified for rare and vulnerable birds, listed in Annex I to the Birds Directive, and for regularly occurring migratory species.
NNR:- (National Nature Reserve)
The aim of an NNR is to secure protection and appropriate management of the most important areas of wildlife habitat, to provide a resource for scientific research and to provide a resource for recreation so long as this does not compromise the wildlife habitat. The majority of NNRs have some permitted access and schoolchildren and students are encouraged to venture in to help them learn about conservation management and see a range of wild animals and plants in their natural habitat.
The statutory purpose of NNRs was revised through the Natural Environment and Rural Communities (NERC) Act to formally recognise the important recreation role the reserves play.
NP:- (National Park)
National Parks are extensive areas each with their own managing authority to conserve and enhance their natural beauty, wildlife and cultural heritage and to promote opportunities for the understanding and enjoyment of their special qualities.
There are a total of 9 national parks in england
1. The Broads 2. Dartmoor 3. Exmoor 4. Lake District 5. New Forest 6. Northumberland 7. North York Moors 8. Peak District 9. South Downs 10. Yorkshire DalesBMP:- (Beach Management Plan)CORNWALL'S COAST
COAST ATLANTIC PROJECT
SITES
THEMES
Beach use
Beach Safety
Licensing Beach and Water Activity
Voluntary Codes of Conduct and Byelaws
ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACTS
Erosion
Beach Cleaning
Dogs
Invasive species
Climate change
PUBLIC PARTICIPATION AND AWARENESS
Surveys
Beach User Forum
Partnerships
Information
Education
Sustainable Tourism
MANAGEMENT FRAMEWORK
Legislation
Ownership and Responsibility
Partnerships
Management Plans
Organisational Structures
CONCLUSIONS
This is a report content from Cornwall county Council, outlining the key factors for managing a beach.
http://www.cornwall.gov.uk/index.cfm?articleid=38834






 Uk territorial waters
Uk territorial waters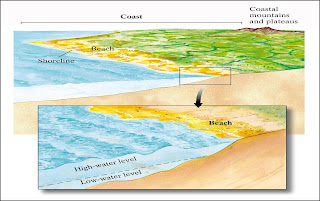
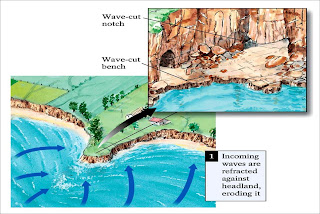
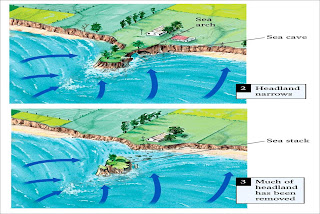 Tides/waves
Tides/waves



